By Sponsored Content Article/Editing: Bruno Venditti
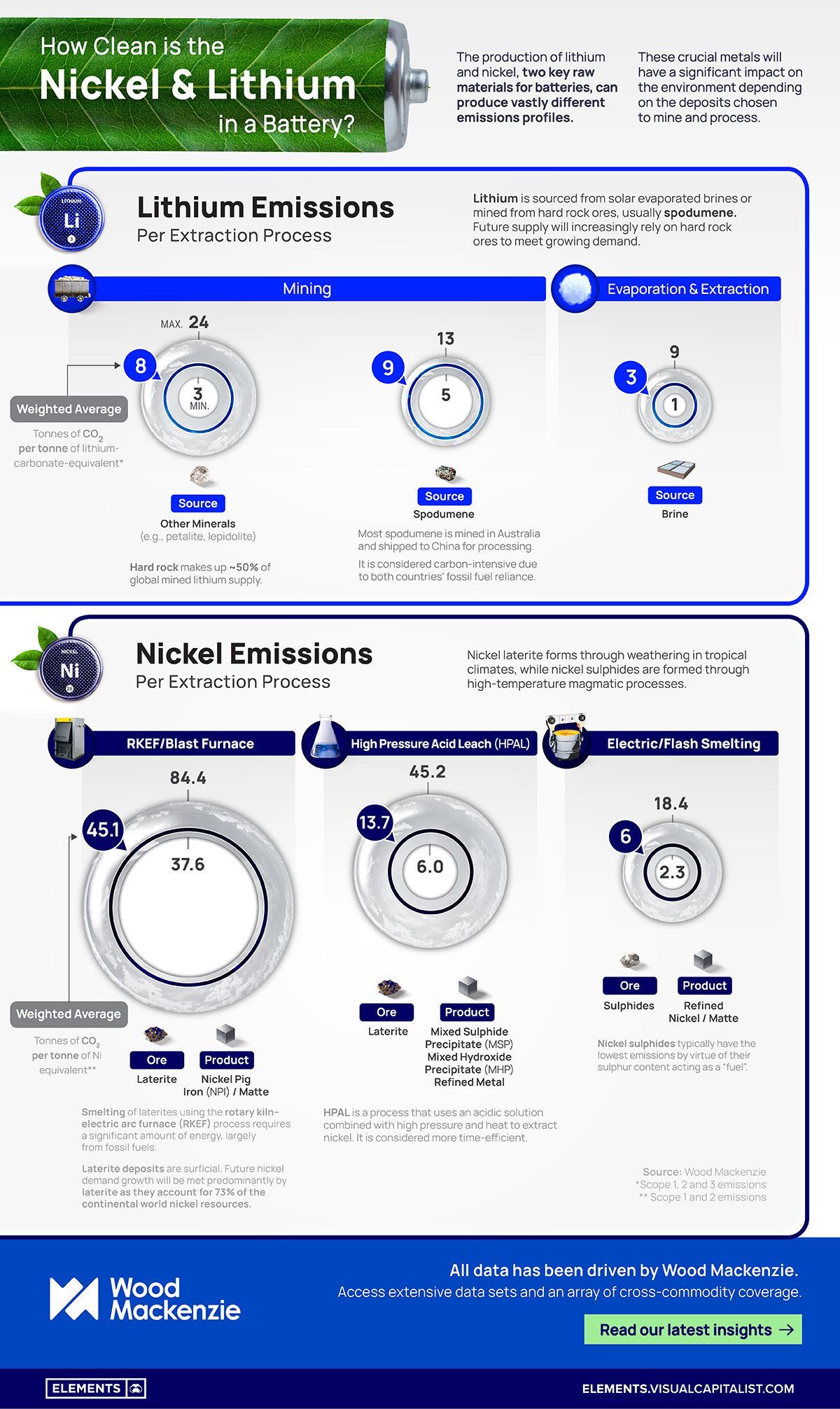
How Clean is the Nickel and Lithium in a Battery?
The production of lithium (Li) and nickel (Ni), two key raw materials for batteries, can produce vastly different emissions profiles.
This graphic from Wood Mackenzie shows how nickel and lithium mining can significantly impact the environment, depending on the processes used for extraction.
Nickel Emissions Per Extraction Process
Nickel is a crucial metal in modern infrastructure and technology, with major uses in stainless steel and alloys. Nickel’s electrical conductivity also makes it ideal for facilitating current flow within battery cells.
Today, there are two major methods of nickel mining:
- From laterite deposits, which are predominantly found in tropical regions. This involves open-pit mining, where large amounts of soil and overburden need to be removed to access the nickel-rich ore.
- From sulphide ores, which involves underground or open-pit mining of ore deposits containing nickel sulphide minerals.
Although nickel laterites make up 70% of the world’s nickel reserves, magmatic sulphide deposits produced 60% of the world’s nickel over the last 60 years.
Compared to laterite extraction, sulphide mining typically emits fewer tonnes of CO2 per tonne of nickel equivalent as it involves less soil disturbance and has a smaller physical footprint:
| Ore Type | Process | Product | Tonnes of CO2 per tonne of Ni equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulphides | Electric / Flash Smelting | Refined Ni / Matte | 6 |
| Laterite | High Pressure Acid Leach (HPAL) | Refined Ni / Mixed Sulpide Precipitate / Mixed Hydroxide Precipitate | 13.7 |
| Laterite | Blast Furnace / RKEF | Nickel Pig Iron / Matte | 45.1 |
Nickel extraction from laterites can impose significant environmental impacts, such as deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil erosion.
Additionally, laterite ores often contain high levels of moisture, requiring energy-intensive drying processes to prepare them for further extraction. After extraction, the smelting of laterites requires a significant amount of energy, which is largely sourced from fossil fuels.
Although sulphide mining is cleaner, it poses other environmental challenges. The extraction and processing of sulphide ores can release sulphur compounds and heavy metals into the environment, potentially leading to acid mine drainage and contamination of water sources if not managed properly.
In addition, nickel sulphides are typically more expensive to mine due to their hard rock nature.
Lithium Emissions Per Extraction Process
Lithium is the major ingredient in rechargeable batteries found in phones, hybrid cars, electric bikes, and grid-scale storage systems.
Today, there are two major methods of lithium extraction:
- From brine, pumping lithium-rich brine from underground aquifers into evaporation ponds, where solar energy evaporates the water and concentrates the lithium content. The concentrated brine is then further processed to extract lithium carbonate or hydroxide.
- Hard rock mining, or extracting lithium from mineral ores (primarily spodumene) found in pegmatite deposits. Australia, the world’s leading producer of lithium (46.9%), extracts lithium directly from hard rock.
Brine extraction is typically employed in countries with salt flats, such as Chile, Argentina, and China. It is generally considered a lower-cost method, but it can have environmental impacts such as water usage, potential contamination of local water sources, and alteration of ecosystems.
The process, however, emits fewer tonnes of CO2 per tonne of lithium-carbonate-equivalent (LCE) than mining:
| Source | Ore Type | Process | Tonnes of CO2 per tonne of LCE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | Spodumene | Mine | 9 |
| Mineral | Petalite, lepidolite and others | Mine | 8 |
| Brine | N/A | Extraction/Evaporation | 3 |
Mining involves drilling, blasting, and crushing the ore, followed by flotation to separate lithium-bearing minerals from other minerals. This type of extraction can have environmental impacts such as land disturbance, energy consumption, and the generation of waste rock and tailings.
Sustainable Production of Lithium and Nickel
Environmentally responsible practices in the extraction and processing of nickel and lithium are essential to ensure the sustainability of the battery supply chain.
This includes implementing stringent environmental regulations, promoting energy efficiency, reducing water consumption, and exploring cleaner technologies. Continued research and development efforts focused on improving extraction methods and minimizing environmental impacts are crucial.
Sign up to Wood Mackenzie’s Inside Track to learn more about the impact of an accelerated energy transition on mining and metals.
Copyright © 2024 Visual Capitalist







